Fifteen UT Health Science Center College of Pharmacy students presented their research posters at the ASHP Midyear Clinical Meeting in Las Vegas earlier this month.
Their dedication and hard work truly exemplify excellence in pharmacy education and research. Take a moment to explore some of the innovative topics they presented!
Evaluation of Specialty Pharmacy Calls

Author: Samantha Townsend. Co-Author(s): Amy Nathanson, Molly Wascher.
Poster Description
Purpose: The specialty pharmacy provides comprehensive, disease state specific, medication management to patients telephonically. Calls to the specialty line are answered by a specialty pharmacy technician, specialty pharmacist, or community pharmacy technician depending on the call reason selected by the caller. The purpose of this project was to identify the types of calls, and which resource was most appropriate to manage the call.
Methods: All call encounters routed to the specialty team from a community pharmacy technician in January 2025 were identified through a report generated in the electronic medical record (EMR). The report was exported to Microsoft Excel and randomized by the patient’s identification number. The first two hundred calls on the report were evaluated through manual chart review to determine the reason for the call and whether that reason was completely addressed by a community pharmacy technician or a member of the specialty team. Calls were categorized as being for one of the following reasons: refill, initial education, financial, delivery issue, clinical management, or miscellaneous. Call encounters were determined to be completed by a community pharmacy technician if the encounter required no further action by the specialty team. If the encounter required a specialty pharmacy technician or a specialty pharmacist to follow up with the patient through a return call or EMR message, then the call encounter was determined to be completed by the specialty team. If there were multiple encounters from the same patient on the same day that were for the same reason, only one encounter was included for analysis. The collected data was analyzed to develop recommendations for improvement.
Results: Out of 194 unique call encounters the most common reason for calls was for refills, which made up 44% (n=88) of the total call volume. Of the 88 refill calls, 43% (n=38) were completed by a community pharmacy technician. Financial calls made up 30% (n=58) of all encounters and 36% (n=21) were completed by a community pharmacy technician. Calls for miscellaneous reasons made up 8% (n=16) of call encounters and 62% (n=10) were completed by a community pharmacy technician. Only 4% (n=9) of call encounters were for delivery issues, and 67% (n=6) were completed by a community pharmacy technician. Initial education and clinical management required the specialty team to complete the encounter 100% of the time. These calls made up 12% (n=23) of all encounters.
Conclusion: Most calls were for refills, and almost half were completely addressed by the community pharmacy technicians rather than the specialty pharmacy team. It was determined that the call routing structure could be improved by preferentially routing refill calls to the community pharmacy technicians and have other calls like those for financial questions and clinical management preferentially go to the specialty pharmacy team. There may have been more financial calls during January as compared to other months. Calls should be reevaluated six months after these routing changes are implemented to determine if they are effective and identify further areas of improvement.
Implementing an Appeal Letter Template in the Electronic Health Record to Expedite Specialty Medication Approval

Author: Kelsie Fadool. Co-authors: Leena Choi, Josh DeClercq, Jessica Fann, Kristen Whelchel
Poster Description
Purpose: Prior authorizations (PAs) for specialty medications used to treat inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are frequently denied for patients prescribed non-formulary agents or non-standard doses. These denials often necessitate a lengthy appeal process which increases administrative burden, delay patient access to therapy, and can lead to worse health outcomes. The purpose of this quality improvement project was to evaluate implementation of a standardized electronic health record (EHR) appeal letter template and medication rationale letters on time to specialty medication approval for patients managed by a Health System Specialty Pharmacy (HSSP).
Methods: This single-center quality improvement project was conducted at an outpatient IBD clinic, where HSSP pharmacists and pharmacy technicians manage specialty medication access. Their responsibilities include completing PAs, composing appeal letters for provider review, and submitting appeals. In June 2023, HSSP pharmacists implemented the use of an EHR appeal letter template and standardized medical rationale content to facilitate the appeal process. A pre-post analysis was conducted using 2 months of data for the pre-implementation (Jan-Feb 2023) and post-implementation (Jan-Feb 2024) cohorts. Records requiring an appeal after a PA denial were included. Primary outcome was the time from PA submission to ultimate outcome (i.e., approval or denial after exhausting the appeal process). Secondary outcomes included time between steps in the appeal process (e.g., PA submission, PA denial, appeal submission, appeal outcome, and ultimate decision), medication prescribed, and reason for PA denial. Categorical variables were described with percentages, while continuous variables were summarized using median and interquartile range (IQR). A multiple ordinal logistic regression was used to model the outcome of time from PA submission to ultimate outcome. Covariates included cohort, indication, (ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease), approval after the first appeal (yes vs. no), and whether the case involved an insurance change, a renewal, or a dose escalation (each coded as yes vs. no).
Results: The pre-implementation cohort included 72 appeals for 71 patients, and the post-implementation cohort included 70 appeals for 70 patients. Eight patients had appeals in both timeframes. Overall time from PA submission to ultimate outcome was similar between the two cohorts (median 14 days, both groups). However, a decrease was observed in time from PA denial to initial appeal submission post-implementation (1 [1 – 3] days) compared to pre-implementation (5 [2-9] days, p < 0.001). In the regression analysis, new prescriptions were 2.7 times more likely to have a longer time to ultimate outcome than renewals (OR = 2.7, 95% Confidence Interval 1.2–5.7, p=0.013). Dose escalation was the most common reason for PA denial (72% pre vs 67% post). Ustekinumab was the most appealed medication in both arms (61% pre vs 43% post). Pre-implementation, 22% of PAs were for new therapies compared to 46% in the post-implementation group. More PAs were completed because of an insurance change pre-implementation (35%) compared to post-implementation (14%). In the subset of records with approval after the first appeal (n=116), median time to approval decreased from 14 (9-26) days pre-implementation to 13 (6-18) days post-implementation (p=0.041).
Conclusion: Using a standardized EHR appeal template and medical rationale letter content significantly reduced the time it took pharmacists to submit appeals and shortened the time from PA denial to ultimate outcome for PAs approved after the first appeal, demonstrating improved process efficiency. However, this intervention did not lead to faster overall approval times, highlighting the need for additional strategies to reduce prior authorization and appeal turnaround time. Additionally, time to approval for new prescriptions consistently took longer than renewals, both before and after implementation, suggesting that further efforts are needed to expedite access for patients initiating new therapies.
Assessment of Student Pharmacist-led MIBG Patient Education Initiative

Author: Monica Lewis. Co-authors: Danaka Hancock, PJ Barker, Kelly Tartera, Kelly Caudle
Poster Description
Purpose: Radiolabeled meta-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) scans are integral in diagnosing, monitoring, and treatment of neuroblastoma and pheochromocytoma. However, there are many common medications which can inhibit proper uptake of the radiotracer, interfering with scan efficacy. To maximize scan clarity and minimize cancellations due to interacting medications, a quality improvement initiative was implemented by student pharmacists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital.
This initiative involved student pharmacists and supervising pharmacists preemptively identifying and contacting patients to ensure the timely discontinuation of interfering medications before their upcoming MIBG scan.
Methods: A single-center, retrospective review was conducted for patients who underwent a MIBG scan from October 1, 2024, to July 31, 2025, at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. This study included all patients who were contacted about their upcoming MIBG scan. Patients were not contacted if they were currently admitted or if their scan date was less than 2 weeks from the date ordered.
The primary objective was to determine the percentage of patients successfully contacted by student pharmacists and their supervising pharmacists at least two weeks before their scheduled MIBG scan. Secondary objectives were to assess the frequency of contact attempts per patient, quantify the number of patients who were not contacted within the time frame, describe any instances of unsuccessful contact, quantify the number of interfering medications identified, and describe and quantify methods of successful contact. An electronic health record (EHR) report identified patients with scheduled MIBG scans. Documented interventions were analyzed to identify the outcome of various outreach activities. Patient contact attempts were analyzed using descriptive statistics in Microsoft Excel based on documented interventions by student pharmacists. Methods and outcomes were quantified to determine the success of contact.
Results: One hundred and twelve patients met inclusion criteria. Thirty-one (36.5%) patients were successfully contacted on first attempt, twenty (23.5%) patients were successfully contacted on second attempt, and thirty-four (40%) patients were successfully contacted on the third attempt. The average number of contact attempts per patient was 2 with a median of 2.1 and mode of 3. Twenty-seven (24.1%) patients were unsuccessfully contacted due to a lack of response from the patient/family. Of the 112 patients included, 109 (97.3%) were not actively receiving medications which would interact with the scan. The predominant method of successful contact was via MyChart messages (n=44, 51.8%), with lower proportions observed for phone calls (n=33, 38.8%), and phone calls with interpreters (n=8, 9.4%). Three (3.6%) patients had an interfering medication identified and notification was sent to the advanced practice provider.
Conclusion: This quality improvement initiative demonstrated the benefit of student pharmacist involvement in medication review prior to MIBG scans. Through this outreach, the vast majority of patients were successfully contacted within 3 attempts. The most successful form of outreach was a MyChart message, which showcases the positive impact of patient portal communication. This success supports continued student pharmacist involvement in medication review and outreach to optimize MIBG scan quality.
Nature’s Prescription: Addressing Deficiencies in Pharmacy Student Knowledge of Natural Products Through Active Learning Strategies
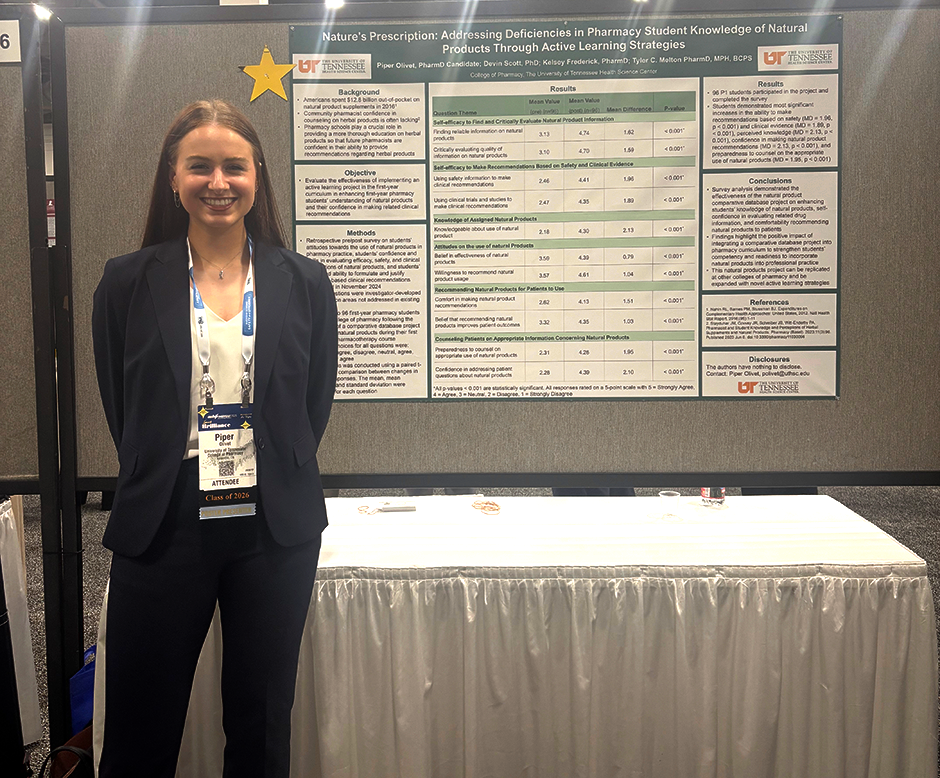

Author: Piper Olivet. Co-Authors: Kelsey Frederick, Devin Scott, Tyler Melton
Poster Description
Purpose: Natural products are an area of increasing interest among the general public; however, they represent a large gap in many pharmacy students’ knowledge. The lack of confidence in making appropriate recommendations regarding these products can impact overall patient care and safety. To address this gap, a natural product drug card project was integrated into the P1 curriculum, allowing students to gain knowledge of and confidence in recommending natural products. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of this curricular intervention in enhancing first-year pharmacy students’ understanding of natural products and their confidence in making related clinical recommendations.
Methods: A retrospective pre/post survey on students’ attitudes towards the use of natural products in pharmacy practice, students’ confidence and skills in evaluating efficacy, safety, and clinical applications of natural products, and students’ perceived ability to formulate and justify evidence-based clinical recommendations was conducted in November 2024. The survey questions were investigator-developed and based on areas not addressed in existing literature. The survey was constructed using Qualtrics and distributed to 96 first-year pharmacy students from one college of pharmacy following the completion of a comparative database project focusing on natural products during their first integrated pharmacotherapy course. The survey comprised eleven questions; two documented self-efficacy to find and critically evaluate natural product information, two to document self-efficacy to make recommendations based on safety and clinical evidence, one to assess knowledge of assigned natural products, two to document attitudes on the use of natural products, two to assess comfortability and perceived importance of recommending natural products for patient use, and two to assess confidence in counseling patients on appropriate information concerning natural products. The response choices for all questions were: strongly disagree, disagree, neutral, agree, and strongly agree. Data analysis was conducted using a paired T-test to draw comparison between changes in pre/post responses. The mean, mean difference, and standard deviation were calculated for each question.
Results: A total of 96 students completed the survey. All participants were members of the P1 class, were currently enrolled in integrated pharmacotherapy I, and had completed the comparative database project on natural products. After completing the project, students demonstrated significant increases in perceived self-efficacy, including the ability to find natural product information (MD = 1.62, p < 0.001) evaluate natural product information (MD = 1.59, p < 0.001), and make recommendations based on safety (MD = 1.96, p < 0.001) and clinical evidence (MD = 1.89, p < 0.001). Students also demonstrated significant increases in perceived knowledge (MD = 2.13, p < 0.001), willingness to recommend natural product usage (MD = 1.04, p < 0.001), and belief in the effectiveness of natural products (MD = 0.79, p < 0.001), and effect of natural product recommendations improving patient outcomes (MD = 1.03, p < 0.001). Lastly, students demonstrated significant increases in comfort and confidence in making natural product recommendations (MD = 2.13, p < 0.001), and addressing patient questions about natural products (MD = 2.1013, p < 0.001), and perceived preparedness to counsel on the appropriate use of natural products (MD = 1.952.13, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Survey analysis demonstrated the effectiveness of the natural product comparative database project on enhancing students’ knowledge of natural products, self-confidence in evaluating related drug information, and comfortability recommending natural products to patients. These findings highlight the positive impact of integrating a comparative database project into pharmacy curriculum to strengthen students’ competence and readiness to incorporate natural products into professional practice. This approach can be replicated at other colleges of pharmacy and be expanded to include additional active learning strategies.
Abemaciclib Dose Escalation in Early Breast Cancer: 12-Month Evaluation of Off-Label Dosing Along with Modifications

Author: Christopher Rodriguez. Co-Authors: Jared Crumb, Josh DeClercq, Chelsea Renfro, Stephanie White
Poster Description
Purpose: Abemaciclib is a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitor approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of early high-risk breast cancer in patients who are hormone receptor (HR)-positive and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative. The FDA-approved dose of 150 mg twice daily is often poorly tolerated, leading to dose holds, reductions, or discontinuations. The purpose of this study is to describe the initial dose, modifications, and time to dose modification in patients with early breast cancer (EBC) who initiate lower than FDA-approved doses of abemaciclib.
Methods: This study was a single-center, retrospective cohort analysis of data collected from an electronic health record, specialty pharmacy management system, and dispensing software at an academic medical center’s outpatient oncology clinic and integrated health-system specialty pharmacy. The patients considered for inclusion had a starting abemaciclib dose of less than 150 mg twice daily for HR+, HER2- early high-risk breast cancer between October 12, 2021 (date of abemaciclib FDA approval in EBC), and August 31, 2023. Patients were followed for 12 months from abemaciclib initiation. Patients were excluded if they had evidence of any other primary malignancy, documented prior use of any CDK 4/6 inhibitor or participation in a clinical trial. Descriptive statistics were utilized to summarize the initial doses, frequency of dose modifications (both escalations and reductions), reasons for dose reductions, time to the first dose modification occurrence of dose holds, and number of patients who achieved FDA-approved dosing.
Results: Among the 47 patients included in the study, all were female and majority were White (n=38, 81%) with a median age of 56 years (interquartile range [IQR], 44–66) at time of initiating abemaciclib. Nearly all patients (n=46, 98%) received prior systemic therapy. More than half began treatment with a starting dose of 50 mg twice daily (n=31, 66%), while remaining patients started at 100 mg twice daily (n=16, 34%). Dose modifications occurred in 46 patients (98%), with the median number of modifications being 2 per patient ([IQR], 1-3). Of 97 total dose modifications, 72 (74%) were dose escalations and 25 (26%) were reductions. Of patients with dose modifications, doses were escalated in 44 patients (44/46, 96%) and reduced in 21 patients (21/46, 46%). Patients had a median of 2 dose escalations (IQR, 1-2) and 0 reductions (IQR, 0-1). Among patients who had dose reductions, 18 (18/21, 86%) had reductions due to common adverse effects. Median time to first dose modification was 28 days (IQR, 16–37). Dose holds occurred in 30 patients (64%); the median duration was 21 days (IQR, 10–28). Within the first year, 28 patients (60%) reached the FDA-approved dose of 150 mg twice daily.
Conclusion: Nearly all patients initiated on lower than FDA-approved abemaciclib dosing escalated the dose at least once. However, half required a dose reduction, most commonly due to adverse effects. Additionally, dose holds were still common. Initiating abemaciclib at a dose lower than 150 mg twice daily in patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative high-risk EBC may facilitate successful escalation to the FDA-recommended dose of 150 mg twice daily. However, further long-term data is needed to assess efficacy and optimal titration strategy.
Clinical Impact of Auto verification within the Emergency Department (ED)
Author: Karissa Suetta. Co-author: Ana Negrete
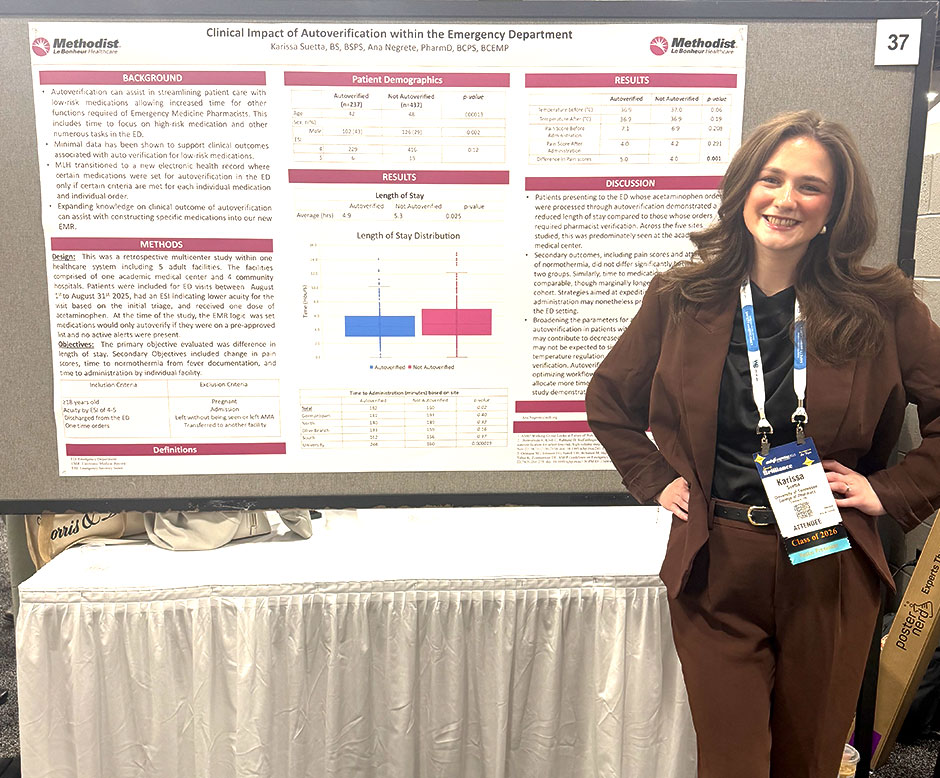

Poster Description
Research In Progress
Purpose: Auto verification is a tool that can assist in streamlining patient care with low-risk medications allowing increased time for other functions required of Emergency Medicine Pharmacists. This includes time to focus on high-risk medication and other numerous tasks in the ED. There has minimal data to support clinical outcomes associated with auto verification for low-risk medications. MLH transitioned to a new electronic health record where certain medications were set for auto verification in the ED. Expanding knowledge on clinical outcome of auto verification can assist with constructing specific medications into our new electronic health record.
Methods: The aim of this Cohort study is to investigate clinical outcomes associated with auto verification of specific medications within the ED. Auto verified medications in the ED from August 1st 2025 to August 31st 2025 will be utilized in this study. The primary outcome is time to discharge for patients who have a medication auto verified compared to those that do not. Secondary outcomes are time to administration, time to documented patient targeted effects including a reduction in pain scores and normothermia from fever. Currently the EMR logic criteria only allows for auto verification if all criteria are met, thus only a small portion of orders qualify for auto verification, even within the same medication or pharmaceutical class. Clinical outcomes of auto verification in the ED may drive optimizing our utilization of this tool.
Comparable Adherence and Viral Suppression Among Youth with Vertically and Horizontally Acquired HIV Receiving Cabotegravir–Rilpivirine with Specialty Pharmacy Support
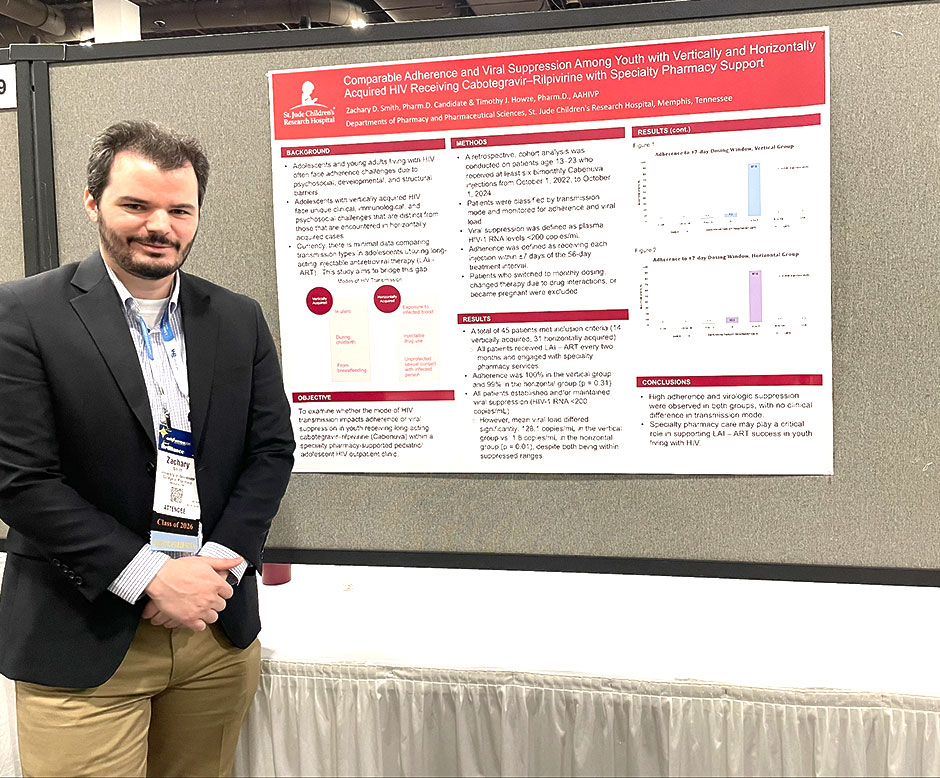
Author: Zachary Smith. Co-author: Timothy J. Howze
Project Description
Purpose: Adolescents and young adults living with HIV often face adherence challenges due to psychosocial, developmental, and structural barriers. This study examined whether the mode of HIV transmission—vertical vs. horizontal—impacts adherence or viral suppression in youth receiving long-acting cabotegravir–rilpivirine (Cabenuva) within a specialty pharmacy-supported pediatric/adolescent HIV outpatient clinic.
Methods: A retrospective, cohort analysis was conducted on patients age 13–23 who received at least six bimonthly Cabenuva injections from October 1, 2022, to October 1, 2024. Patients were classified by transmission mode and monitored for adherence and viral load. Adherence was defined as receiving each injection within ±7 days of the 56-day treatment interval. Patients who switched to monthly dosing, changed therapy due to drug interactions, or became pregnant were excluded.
Results: A total of 45 patients met inclusion criteria (14 vertically acquired, 31 horizontally acquired). Adherence was 100% in the vertical group and 99% in the horizontal group (p = 0.31). All patients established and/or maintained viral suppression (HIV-1 RNA < 200 copies/mL). However, mean viral load differed significantly: 128.1 copies/mL in the vertical group vs. 1.8 copies/mL in the horizontal group (p = 0.01), despite both being within suppressed ranges.
Conclusion: High adherence and virologic suppression were observed in both groups, with no clinical difference in transmission mode. Specialty pharmacy care may play a critical role in supporting long-acting injectable antiretroviral therapy (LAI – ART) success in youth living with HIV.
Comparison of Adverse Event Profiles in Biologics Produced in SP2/0 and CHO Cell Lines
Author: Holly Angell. Co-author: Harman Thind
Project Description
Purpose: Monoclonal antibodies produced in murine myeloma (Sp2/0) and Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell lines differ in glycosylation, which can influence immunogenicity. This study evaluated whether Sp2/0-derived biologics exhibit higher reporting proportions of adverse events than CHO-derived counterparts. Post-marketing data from the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) and clinical trial outcomes were compared for matched drug pairs to quantify reporting frequencies of gastrointestinal (GI) events, rash, infusion reactions, and anaphylaxis. This retrospective analysis aimed to identify trends and outliers in safety profiles across cell-line platforms, using FAERS as a real-world pharmacovigilance source.
Methods: FAERS 2024 data were retrieved for all adverse event submissions related to biologics of interest, categorized by manufacturing cell line (Sp2/0 or CHO). Five Sp2/0-derived and five CHO-derived antibodies were selected and matched by indication, including colorectal cancer, Crohn’s disease, neuroblastoma, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriasis. Drugs without a direct comparator or those discontinued were excluded. To ensure consistency in therapeutic use, only brand-name FAERS entries were analyzed. Reports for nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea were grouped into a single GI events category, while rash, infusion reactions, and anaphylaxis were assessed separately. Seizure and pulmonary fibrosis were included as non-immunogenic control events to evaluate potential reporting bias across cohorts. For each biologic, the proportion of total reports attributed to each category was calculated. In addition, a pairwise comparison was performed between matched Sp2/0 and CHO-derived biologics with identical or overlapping indications to assess relative differences in adverse event proportions within each therapeutic area. The combined dataset allowed a descriptive comparison of adverse event trends between Sp2/0 and CHO-derived biologics across real-world and clinical trial contexts.
Results: Across all matched FDA indications, Sp2/0-derived biologics showed higher proportions of reported GI events, rash, infusion reactions, and anaphylaxis compared to CHO-derived biologics. In FAERS, Sp2/0 products reported 49.6% GI events versus 18.9% for CHO, 27.3% versus 9.0% for rash, 26.7% versus 7.6% for infusion reactions, and 0.82% versus 0.36% for anaphylaxis, corresponding to approximately 2.6, 3.0, 3.5, and 2.2 fold higher reporting, respectively. Pairwise comparisons across matched indications showed a consistent increase in anaphylaxis for Erbitux (3.7%) vs Avastin (0.4%), Remicade (1.0%) vs Entyvio (0.6%), Simponi (0.5%) vs Humira (0.4%), and Stelara (0.7%) vs Skyrizi (0.2%). The only exception was Danyelza (CHO), which showed 26.8% anaphylaxis versus 0% for Unituxin (Sp2/0). This outlier can be explained by the anti-GD2 class effects, where infusion-related immune activation can produce reactions clinically reported as anaphylaxis or hypersensitivity, which may help explain elevated anaphylaxis reporting despite CHO cell-line origin.
Conclusion: SP2/0-derived monoclonal antibodies showed consistently higher reporting of GI events, rash, infusion reactions, and anaphylaxis compared with CHO-derived biologics. The exception of higher anaphylaxis with CHO-derived Danyelza suggests that drug-specific factors may outweigh cell-line effects. Despite broader CHO use, their proportional adverse event rates remained lower, supporting the idea that manufacturing cell lines can affect immunogenicity. Although FAERS data cannot confirm causality, these findings are consistent with known glycosylation-related hypersensitivity, such as α-Gal mediated allergy in SP2/0 products. Further monitoring and prospective studies are needed to confirm these trends.
Assessing the adverse drug event profiles of commonly used medications in the United States
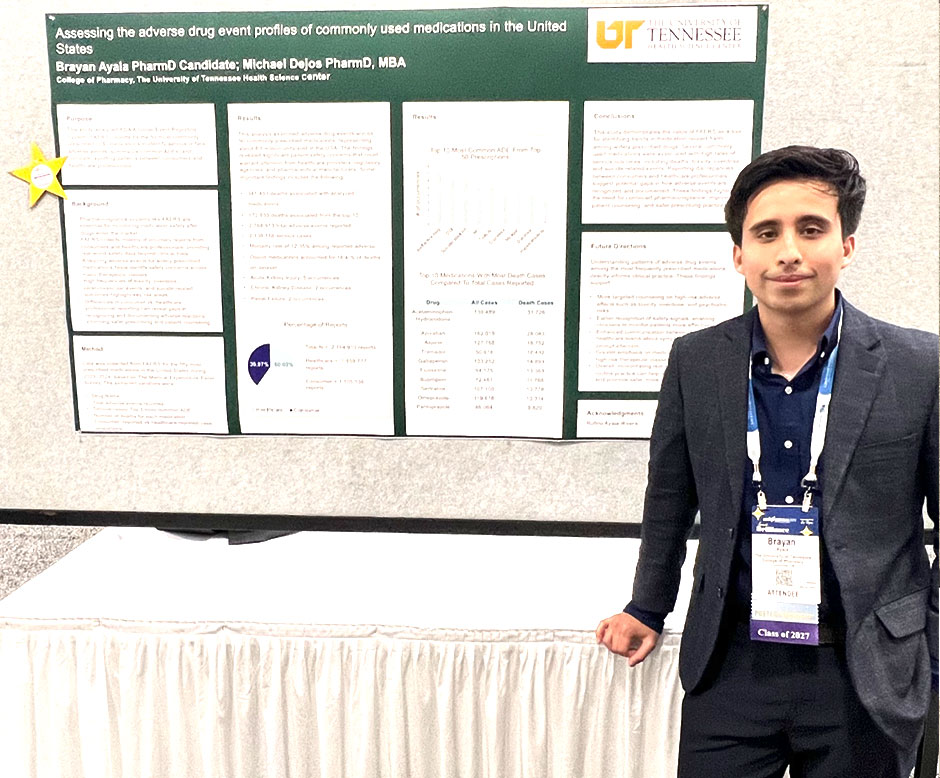
Author: Braya Ayala. Co-author: Michael Dejos
Project Description
Purpose: The objective of this study was to evaluate patterns of drug-associated adverse events reported in the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) for the 50 most commonly prescribed medications in the United States. The analysis aimed to identify the most commonly prescribed drugs in the United States, characterize common adverse drug event trends, and compare reporting differences between consumers and healthcare professionals.
Methods: Data was collected from FAERS for the 50 most prescribed medications in the U.S. market during 2023–2024, as determined from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. Extracted variables included drug name, number of reported deaths, consumer- versus healthcare-reported case proportions, the three most frequently reported adverse effects per drug, and the AHFS classification. Data was compiled into a standardized dataset and analyzed for trends in mortality, adverse events, and reporting patterns. Comparative analyses were performed between consumer- and healthcare-reported cases to highlight potential discrepancies in adverse event recognition and reporting.
Results: Among the top 50 prescribed drugs, oxycodone was associated with the highest number of deaths (68,883), followed by acetaminophen (37,726), apixaban (28,083), and prednisone (27,324). Opiate agonists, as classified by AHFS, emerged as the most high-risk drug category. Opioid agents such as oxycodone and tramadol demonstrated strong associations with dependence (oxycodone: 109,741 cases; tramadol: 22,316 cases) and overdose (oxycodone: 55,529 cases; tramadol: 14,007 cases). Acetaminophen was linked to significant toxicity (18,463 cases) and overdose (11,802 cases), while alprazolam and citalopram were notably associated with suicide (7,796 and 4,563 cases, respectively). Apixaban was primarily associated with cerebrovascular complications, but not with dependence or overdose. Reporting trends indicated that most oxycodone-related deaths were consumer-reported (72.6%), whereas acetaminophen- and prednisone-related deaths were predominantly healthcare-reported.
Conclusion: This study highlights the utility of FAERS in identifying medications and characterizing patterns of adverse drug events. Oxycodone, acetaminophen, and tramadol were most strongly associated with dependence, overdose, or toxicity, while psychiatric medications showed notable associations with suicide. Differences in consumer versus healthcare reporting suggest potential gaps in adverse event recognition and communication. These findings underscore the importance of leveraging pharmacovigilance data to guide regulatory action, inform safer prescribing practices, and enhance patient education to reduce preventable harm
Assessment of decontamination protocol for hazardous drugs for two models of 3D medication printers

Author: Jennifer Hampton. Co-author: Cindy Brasher
Project Description
Purpose: Three-dimensional (3D) printing is transforming pharmaceutical manufacturing by enabling the creation of personalized medications tailored to individual patient needs. As this technology is introduced into pharmacy practice, robust cleaning protocols are essential to maintain product integrity and prevent cross-contamination—particularly when handling hazardous or high-potency compounds. Cleaning agents must be compatible with the varied materials used in 3D printing, and all cleaning procedures must be rigorously validated to ensure compliance with regulatory and quality standards.
Methods: Prior to the integration of 3D printing for hazardous drug compounding, the Department of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Services mandates the development of standardized cleaning procedures to ensure the safety of both patients and compounding personnel. To assess potential contamination post-compounding, fluorescein dye is incorporated during test runs on the M3DIMAKER® and CurifyLabs® 3D printers. Areas showing fluorescein dye residue are subsequently wipe-sampled following cyclophosphamide printing. After initial sampling, the printers undergo decontamination, and wipe sampling is repeated to evaluate the effectiveness of the cleaning protocols.
Evaluating the Cost-Effectiveness and Clinical Outcomes of Different Hepatitis C Virus Testing Timeframes in Hospitalized Patients

Author: Calvin Mai. Co-authors: Nathan Summers, Clark Allen, Drew Armstrong
Project Description
Purpose: Hepatitis C virus is a chronic infection that, if left untreated, may progress to cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver failure. Although curative therapies exist, delayed diagnosis and inconsistent inpatient screening limit timely treatment. Guidelines recommend universal one-time testing for adults aged 18–79; however, the optimal timing for hospital-based screening remains unclear. This study aims to evaluate whether the timing of Hepatitis C Virus screening impacts detection rates, linkage to care, and cost-effectiveness.
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study of adult patients aged 18–79 admitted through the emergency department between September 29, 2020, and March 29, 2022. Eligible patients include anyone admitted through the emergency department with an HCV screening collected. Exclusion criteria include age younger than 18 or older than 79, length of stay shorter than 24 hours, hospice or palliative care status, or incarceration. Data will be extracted from electronic health records and analyzed in Microsoft Excel. Primary outcomes include (1) HCV case detection rates and (2) linkage-to-care and treatment initiation. A secondary exploratory analysis will estimate cost-effectiveness by comparing relative testing costs and completed linkage-to-care per screening timeframe, using available hospital cost data. Results will help determine whether earlier admission screening provides clinical or economic advantages compared with delayed testing.
Appropriate Use of Eculizumab for Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy After Guideline Implementation in a Pediatric Specialty Hospital

Author: Madeline Matheson. Co-authors: Madison Cole, Melissa Hines, Timothy Jacobs, Delia Allen.
Project Description
Purpose: Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) occurs in up to 20% of patients following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation resulting in complement activation which is often associated with multi-organ damage. Eculizumab, a terminal complement inhibitor, is used to mitigate these effects but presents challenges due to its high cost, need for complement monitoring, and a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) requirement intended to reduce the risk of serious meningococcal infections. For these reasons, institutional guidelines have been implemented to support appropriate prescribing practices. This retrospective study evaluates adherence to institutional guidelines for ordering, initiating, and discontinuing eculizumab therapy.
Methods: A retrospective chart review was conducted to evaluate adherence to institutional guidelines for eculizumab use in patients at a pediatric oncology research hospital. Data was collected from June 2022 through July 2025. Patients who received eculizumab during this period were identified and classified by treatment indication. Comprehensive chart reviews were conducted to assess transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (TA-TMA) risk factors, pre-therapy complement levels, total number of eculizumab doses administered, and doses given TA-TMA was resolved or excluded as the underlying cause of symptoms.
Complement activity was monitored using CH50 (total) and soluble C5b-9 (sC5b-9; terminal) levels. For this study, complement suppression was defined as the first instance of sC5b-9 within normal limits. CH50 and sC5b-9 were used to monitor complement activity, and therapy appropriateness was evaluated based on suppression criteria and clinical stabilization. Eculizumab serum concentrations were collected when available.
Descriptive statistics were used to compare patient demographics, treatment indications, complement monitoring patterns, and adherence to recommended therapeutic guidelines.
Case Report: Double Trouble: Solifenacin and Fluoxetine’s Unexpected QT Prolongation Synergy

Author: Mark Miller. Co-authors: Riley Wolf, Farhan Aslam, Kelly C. Rogers
Poster Description
Introduction: Several drug therapies are associated with prolongation of the QT interval which increases the risk of a characteristic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, torsades de pointes (TdP). Given that TdP is life threatening, implicated medications should be promptly identified and removed and immediate treatment should be provided. Treatment strategies may include correction of electrolyte abnormalities, intravenous magnesium sulfate, increasing the heart rate, and electrical cardioversion. This report describes the use of two medications known to prolong the QT interval in a patient suspected of experiencing TdP: solifenacin, an anticholinergic medication used to treat overactive bladder and fluoxetine, a SSRI indicated for depression and anxiety.
Case: A 71-year-old female with a history of osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, depression, iron deficiency anemia, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, chronic urinary tract infections, and overactive bladder, presented to the emergency department after losing consciousness in her home and sustaining a subarachnoid hemorrhage from the fall. On admission to the Trauma ICU, her ECG revealed a severely prolonged QTc (Bazett: 618 msec, Fredericia: 598 msec). It was discovered with a medication reconciliation that not only did the patient take two QT-prolonging drugs (solifenacin and fluoxetine) concurrently, but she also reported to taking fluoxetine 40mg three times a day rather than her prescribed dose of 40 mg once daily, due to her feeling that it wasn’t helping her enough. The patient reported worsening dizziness the few days prior to the fall, leading to the suspicion that she potentially experienced TdP.
Discussion: While fluoxetine doesn’t contribute to QT prolongation as much as other SSRIs, co-administration with other QT prolonging medications should be done with extreme caution, especially in patients with increased risk of TdP (such as females, elderly, and patients with underlying cardiomyopathy). This patient required more frequent monitoring to assess medication compliance, as this event could have been avoided if it was discovered sooner that she was tripling her fluoxetine dose.
Survey Analyzing Tube Feed Practices Among Nursing Staff at a Large Academic Medical Center and Implication on Insulin Administration

Author: Maryam Moradi. Co-Author: Marissa Belch
Poster Description
Purpose: This survey was created to better understand how nursing staff uses Epic to manage tube feeds. This survey focused on figuring out how tube feed orders are documented, communicated, and adjusted, especially when they are held or orders lack clear instructions. We wanted to further explore nursing practices around adjusting or holding insulin when tube feeds are held. Insights from this survey will help guide the development of Epic-based tools to support nursing decision-making and improve patient safety.
Methods: For this study, we developed a REDCap survey consisting of six questions, including both multiple-choice and fill-in-the-blank formats. The survey was distributed to a group of “Diabetes Nurse Champions” as well as a select group of nurses from various units across the hospital. The Diabetes Nurse Champions are nurses who have completed specialized training focused on diabetes care, insulin types, and glucose monitoring.
The goal of the survey was to gather insights into how nurses use Epic when managing patients on tube feeds, specifically how they document, respond to tube feed rate changes and holds, and act when provider instructions are unclear. We then explored their practices around administering or holding insulin when tube feeds are paused.
Results: A total of 30 responses were collected over a two-week period. Once the survey closed, the data was compiled and analyzed, with key themes and findings presented to the hospital’s Diabetes and Glycemic Oversight Committee. The goal of this presentation was to initiate discussion on potential Epic-based interventions, such as the implementation of clinical decision support tools, to better guide nursing staff in managing tube feed-related care and insulin administration. This collaborative effort aimed to improve patient safety and ensure consistent practices across units. A workgroup is currently underway to create an insulin order panel specific to “insulin for tube feeds” with specific instructions on how to manage if tube feeds are held.
Conclusion: This survey highlighted variability in how nurses manage tube feeds and associated insulin administration, particularly when provider instructions are unclear. Findings emphasized the need for improved clinical decision support within Epic to guide nursing actions. In response, a workgroup is developing an insulin order panel specific to “insulin for tube feeds” with specific instructions on how to manage if tube feeds are held, aiming to standardize care, reduce errors, and enhance patient safety.”
Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis Use Evaluation in Patients Transferred from a Critical Care Unit to a General Medicine Floor at a Pediatric Tertiary Care Hospital
Author: Nicholas Shute. Co-Author: Megan W. Woods
Poster Description
Purpose: Acid suppression is frequently utilized as prophylaxis against stress ulcers in pediatric patients admitted to intensive care units due to increased concerns for serious gastrointestinal complications. Stress ulcer prophylaxis is typically discontinued upon transfer to general medicine floors as the risk for gastrointestinal complications is generally lower. The purpose of this retrospective study is to evaluate the frequency of continuation of acid suppression in patients transferred from a critical care unit to a general medicine floor. Additionally, this study will evaluate concomitant medications and patient characteristics that might warrant continuation of stress ulcer prophylaxis upon transfer.
Methods: A retrospective review of the electronic medical record was conducted from July 30, 2024 through January 29, 2025 at Le Bonheur Children’s Hospital, a tertiary care center. Patients were included if they were admitted to a critical care unit and received acid suppression therapy. Collected data included patient age, sex, weight, admitting diagnosis, total length of hospital stay, nutrition status, recent surgery history, and acid suppression drug class. Concomitant medications including steroids, scheduled non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anticoagulants, and antiplatelets were also assessed. Patients were excluded if they were taking acid suppression prior to admission, on acid suppression for an indication other than stress ulcer prophylaxis, discharged directly from the critical care without transferring to a general medicine floor, or never received the ordered medication. The primary outcome is whether stress ulcer prophylaxis was continued upon transfer and discharge.
